Sidebar blog
Post Date
September,
08
2025
Thinking about replacing or upgrading your battery? Don’t hit “buy” just yet. Matching an e bike battery is a mix of mechanical fit, electrical specs, and communication protocol. Look‑alike shells don’t guarantee it will work; perfect dimensions don’t mean it will power on. Follow this step‑by‑step checklist.
- Start with the exterior (case/base/connectors/lock) 🔍
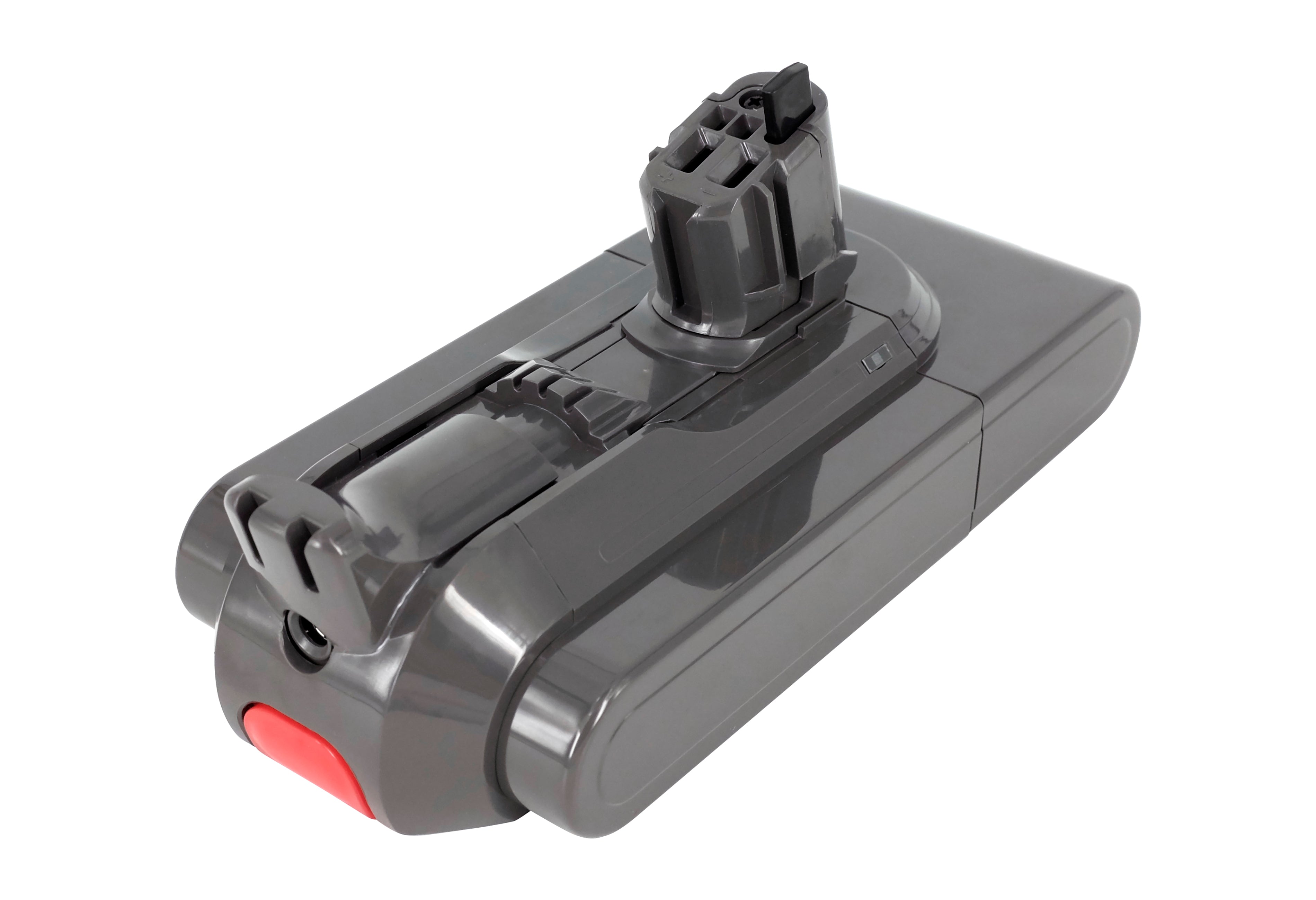
- Case style:
- Downtube (e.g., “Shark/Hailong,” “Dorado/rail,” integrated in‑frame)
- Rear‑rack packs, seatpost/water‑bottle style, etc.
- Mounting method:
- Rail/slide base or bolt‑on? Is the base type the same (e.g., Reention Hailong/Dorado series)?
- Ports and features:
- Are discharge and charge ports (and any small signal pins) on the same side and in the same location?
- Key lock, handle, LED fuel gauge, power button—do their positions line up?
- Pro tip:
- Many brands share similar shells, but internal pinout, pin count, and base revisions can differ. Photograph clearly before comparing.
- Compare dimensions (clearance is king) 📏
- Key dimensions:
- Length, width, height (include the tallest point/handle/protrusions)
- Base rail length and hole spacing; latch position to end distance
- Pin center height; distance from ports to case edges (to avoid interference)
- Allow clearance:
- Leave 5–10 mm of slack to clear welds, cable guides, BB covers, etc.
- Photo angles to capture:
- Top/side/bottom (include the base), connector close‑ups (with a ruler or card for scale)
- Compare the brand and exact model (ecosystem compatibility) 🧩
- Identify your drive system:
- Turnkey systems (Bosch / Yamaha / Shimano / Brose / Specialized, etc.) are typically closed ecosystems; batteries and protocols are tightly coupled—cross‑brand swaps are not recommended.
- Bafang: older BBS kits are often UART and external; M‑series (M600/M620, etc.) commonly use CAN with stricter requirements.
- Generic motors/controllers: many have no comms or simple serial; matching voltage/current/connector can be enough.
- Don’t skip electrical specs:
- Voltage must match controller rating (common: 36V, 48V, 52V). “Higher” is not “better”—it can damage the controller.
- Capacity (Ah) = range; higher capacity is heavier—confirm frame and base can handle the weight.
- Current: BMS continuous/peak discharge must meet or exceed controller demand to avoid limiting or shut‑off.
- How to identify models:
- Check labels on the original battery, controller, and display (model/year), and the base/rail. These often dictate compatibility.
- Communication protocol (the invisible deal‑breaker) 🛡️
- What it is:
- The “handshake language” between the battery’s BMS and the controller—CAN, UART, LIN, SMBus, and vendor‑specific variants.
- Why it matters:
- Same shell, different protocol; same pins, different pinout—both can mean “fits but won’t power on / throws errors / limits output.”
- Quick heuristics:
- Only 2 large power pins often means no comms; 3–5 pins or extra small pins often indicate data and/or temp/wake lines.
- But never rely on pin count alone—confirm brand/model/year and protocol version.
- Real‑world reminders:
- Dorado shells across brands may use different CAN parameters or pin maps; Bosch Smart System is not backward‑compatible; Bafang M‑series differs from BBS kits.
Pre‑purchase checklist ✅
- Case type, base model, and latch position
- Overall L/W/H + rail length and hole spacing + port‑to‑edge distances
- Frame cavity space and cable routing clearances
- Discharge/charge connector types and pin count (including polarity)
- Rated voltage and max charge voltage (e.g., 54.6V/58.8V)
- BMS continuous/peak discharge current
- Drive system brand and controller/display model
- Communication protocol and pinout
- Charger plug/spec compatibility
- Certifications/support (e.g., CE, UL 2271/2849) and IP rating
Not sure? Send these to PowerSmart support and let them match it faster 📨
- Must‑have info:
- Clear label photo of the original battery (voltage/capacity/model/barcode/year)
- Three‑view shots of the pack + base/rail + connector close‑ups (with a ruler)
- Frame mounting area photos (to check interference) and base hole spacing
- Motor/controller/display labels or model numbers (e.g., Bafang M600, Bosch Gen4)
- Your target range or capacity preference
- Dimension template (copy and fill):
- L × W × H (max envelope): ____ × ____ × ____ mm
- Base rail length: ____ mm; hole spacing: ____ mm; latch‑to‑end: ____ mm
- Discharge port: type/pin count/polarity; distance to left/bottom edge: ____ / ____ mm
- Charge port: type/pin count; location: ____
- Usable frame cavity space: ____ × ____ × ____ mm
Common pitfalls to avoid ⚠️
- “Looks the same, so it fits” — No. Protocols, pinouts, and base revisions can ruin the party.
- “Higher voltage = better” — No. Over‑voltage can brick a controller or trigger errors.
- “More capacity is always better” — Not necessarily. Consider weight, balance, base strength, and charge time.
- “If it plugs in, it works” — Not guaranteed. Polarity, pinout, or protocol mismatches can cause faults.
Safety tips 🧯
- Power down before working; avoid short circuits. Don’t touch pins with metal tools.
- Use the matching charger only; avoid heavy rain/submersion and high heat.
- For storage/shipping: 30–60% state of charge, cool/dry, away from combustibles.
If you’d like, send your photos and specs to PowerSmart support—they’ll verify appearance, dimensions, brand/model, and protocol in one go. That’s how you pick a battery with confidence.








Leave a comment